osteoblast|osteoblast meaning : iloilo In cell cultures, many osteoblast precursors form osteocyte-like connections (Fig. 3E); how this affects further cell differentiation is uncertain, but there definitely is high production of sclerostin in human osteoblast cultures (Table 1), and sclerostin inhibits mineralized bone formation. 113,114 Potential methods for limiting effects in . webFree Trans Mega Files. 10 898 subscribers. Free trans mega files!! Just follow the steps once you click the link. View in Telegram. Preview channel.
0 · osteoblasts location
1 · osteoblasts functions
2 · osteoblast vs osteocyte
3 · osteoblast vs osteoclast origin
4 · osteoblast vs osteoclast
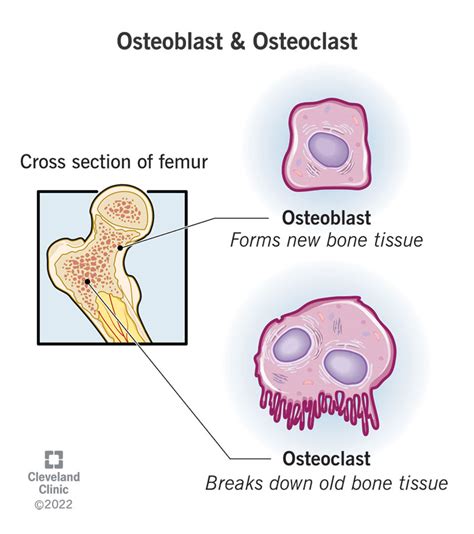
5 · osteoblast picture
6 · osteoblast meaning
7 · osteoblast in humans
Resultado da 1080p. Caiu na Net novinha safada de São Paulo pedindo pra socar na buceta dela e gemendo alto na rola do namorado no motel. 6 min .
osteoblast*******Learn how osteoblasts and osteoclasts work together to form new bone cells and break down old or damaged bone tissue. Find out about common conditions and disorders that affect these cells and . Osteoblasts are cells that produce and mineralize bone matrix. They originate from osteogenic cells in the periosteum and . Osteoblast differentiation requires a multitude of steps from a stem cell differentiating into a mature osteoblast. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and skeletal stem cells (SSCs) have both been .
Osteoblast differentiation from MSCs also appears to be a feed-forward phenomenon as demonstrated by the fact that co-culturing MSCs with mature osteoblasts promotes MSC osteogenic differentiation [20,21]. Intriguingly, this feed-forward mechanism is at least partially mediated by soluble factors, .
osteoblast In cell cultures, many osteoblast precursors form osteocyte-like connections (Fig. 3E); how this affects further cell differentiation is uncertain, but there definitely is high production of sclerostin in human osteoblast cultures (Table 1), and sclerostin inhibits mineralized bone formation. 113,114 Potential methods for limiting effects in .The osteoblast, the bone cell responsible for forming new bone, is found in the growing portions of bone, including the periosteum and endosteum. Osteoblasts, which do not divide, synthesize and secrete the collagen matrix and calcium salts. As the secreted matrix surrounding the osteoblast calcifies, the osteoblast becomes trapped within it.Other osteoblast precursor cells, such as Dlx5 + and Osx + cells on the bone surface, are concomitantly recruited to the injury site and collectively participate in regeneration . In complete fracture repair involving the formation of the fracture callus, chondrocyte-to-osteoblast transformation plays an important role in bone repair.
The ultimate fate of the mature osteoblast is the development of the osteocytes, bone lining cells, or apoptosis [35, 36]. Some sort of TUNEL-positive structures are observed inside the osteoblast vacuoles, indicating that these cells have the capability of engulfing and degrading the apoptotic bodies [37].
osteoblast meaning In this review, we discuss well-established pathways of osteoblastic differentiation, i.e., the classical ones committing mesenchymal stromal cells to osteoblast, and then osteocytes as well as recently emerged players. In particular, we discuss micro (mi)RNAs, long non-coding (lnc)RNAs, circular (circ)RNAs, and extracellular vesicles, .Osteoblast and osteocyte morphology by transmission electron microscopy. (A) Active osteoblast on the bone surface in which the matrix is still unmineralized (osteoid). Golgi vesicles are located adjacent to the nucleus and abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum is observed throughout the cytoplasm. Magnification, 8000×.
Identification of osteoclast and osteoblast gene signatures. The bone was centrifuged to remove loosely adherent marrow; the remaining bone sample (bone and cells on the bone surface, e.g .
RSS Feed. Osteoblasts are one of the three cell types found in vertebrate bones. Osteoblasts synthesise the bone collagen matrix of the bone and also participate in matrix mineralisation, which .osteoblast osteoblast meaning Osteoblast differentiation is regulated through the successive activation of signaling molecules by a complex interplay of extracellular signals such as bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and .Abstract. Bone is constantly being remodelled in a dynamic process where osteoblasts are responsible for bone formation and osteoclasts for its resorption. Osteoblasts are specialized mesenchymal cells that undergo a process of maturation where genes like core-binding factor alpha1 (Cbfa1) and osterix (Osx) play a very important role.
Conversely, osteoclasts also influence formation of bone by osteoblasts via the d2 isoform of vacuolar (H+) ATPase (v-ATPase) V0 domain (Atp6v0d2), complement component 3a, semaphorin 4D or microRNAs. In addition, cytokine released from the resorbed bone matrix, such as TGF-β and IGF-1 also affects the activity of osteoblasts.
Osteoblasts are cells that secrete the material for bone formation. The process of making new bone is called osteogenesis. There are five cells that work together to regulate bone formation and .
NF-kappa B. Osteoblasts are mononucleated cells that are derived from mesenchymal stem cells and that are responsible for the synthesis and mineralization of bone during initial bone formation and later bone remodelling. Osteoblasts also have a role in the regulation of osteoclast activity through the receptor ..
Osteoblast-osteoclast communications are essential for fine-tuning of bone remodeling during bone homeostasis. (1) Osteoblasts and osteoclasts have direct contacts through the interactions between EFNB2-EPHB4, FAS-FASL and NRP1-SEMA3A to regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. (2) Osteoclast-mediated bone .
The second film in the bone biology series describes the role and functions of the cells responsible for breaking down bone tissue (osteoclasts) and building. Bone formation is a highly energy-demanding process that can be impacted by metabolic disorders. Glucose has been considered the principal substrate for osteoblasts, although fatty acids are also .
13 de jun. de 2019 · The term 'tiki-taka' was actually created by Andres Montes, a Spanish commentator who used it to describe the playing style's accurate and elegant passes. In Basque it means “taking quick, light .
osteoblast|osteoblast meaning